ANTIMICROBIAL TECHNOLOGIES
Introduction to Antimicrobial Protection & Microbes
Microbes are microscopic life forms, usually too small to be seen by the naked eye. Although many microbes are single-celled, there are also numerous multi-cellular organisms.
Microorganisms are very diverse and include bacteria, fungi, and algae. Microorganisms live in all parts on the earth where there is liquid water, including hot springs, on the ocean floor, high in the atmosphere and deep inside rocks within the Earth’s crust. Certain microbes have adapted to withstand unusual environmental conditions, including extreme pressure, temperature, acidity, and radiation. These microscopic organisms are found in plants and animals as well as in the human body. Wherever we are, we have the company of microbes.
ANTIMICROBIAL PROTECTION & BACTERIA
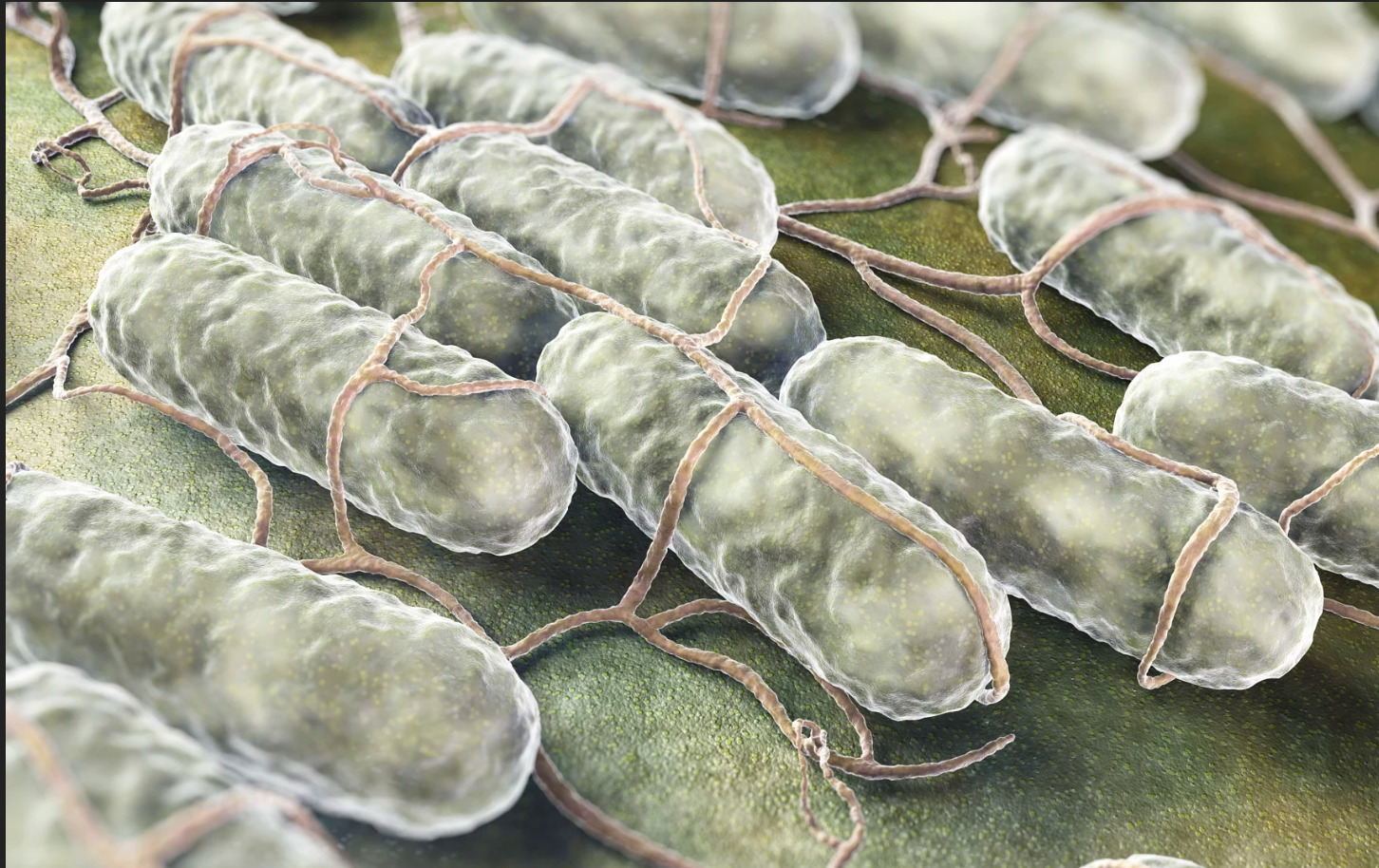
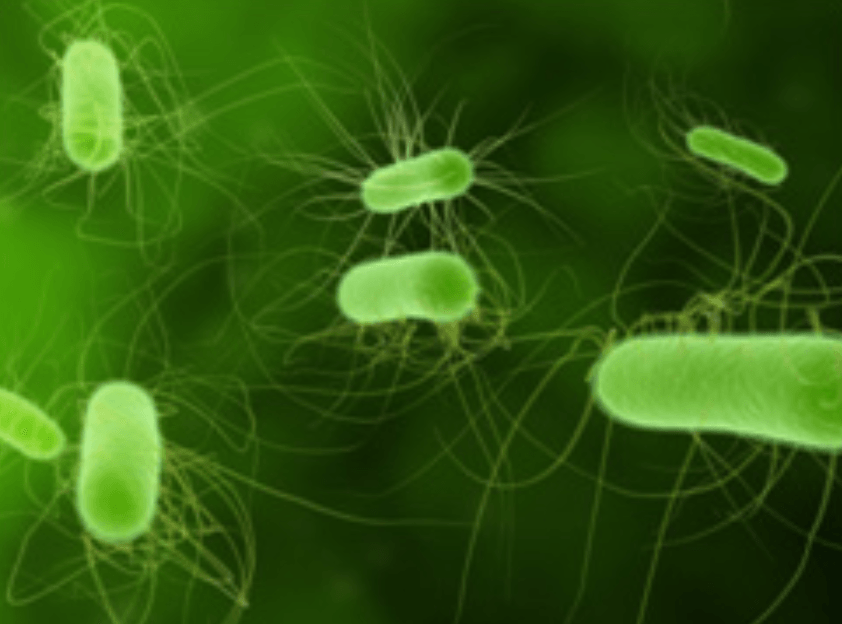
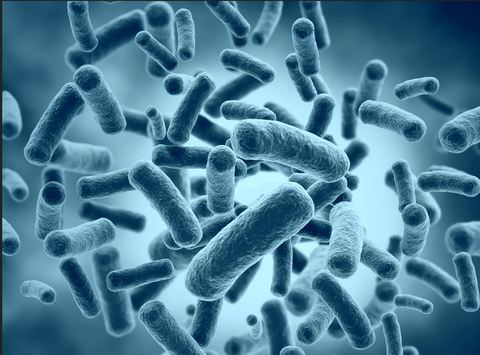
Bacteria are among the earliest forms of life. They first appeared on Earth billions of years ago. Bacteria are single-celled micro-organisms that lack a nuclear membrane. Under a microscope, bacteria look like balls, rods, or spirals. Similar to all living cells, each bacterium requires food for energy and building materials. There are countless bacteria on Earth. Some cause diseases, infections and unpleasant odors. However, most are harmless and many are beneficial to humans.
ANTIMICROBIAL PROTECTION & FUNGI
Fungi are multi-celled organisms with structures analogous but not identical to plants. They can be found in air, in soil, on plants, and in water. Thousands, possibly millions, of different types of fungi exist on Earth. The common types are mushrooms, yeast, mold, and mildew. Some live in the human body, usually causing illness. Fungal diseases are called mycoses. Mycoses can affect human skin, nails, body hair, internal organs such as lungs, and body systems such as the nervous system. Aspergillus fumigatus, for instance, can cause aspergillosis, a fungal infection in the respiratory system.
Fungi obtain nutrients, eliminate waste, and reproduce in a much more complex way than bacteria. They have structures that perform these specialized functions so that disrupting one functions does not mean disrupting other critical functions.
Consequently, the simple disruption of some cellular functions will not necessarily be fatal to fungi. There are more cells and centers for vital functions than there are for the single cell bacteria.

Fungi
One well-known fungi type is mold, which can be found everywhere, and there are no practical ways to entirely abolish mold spores in the indoor environment. The best protection against mold is moisture control to prevent it from breeding.
ANTIMICROBIAL PROTECTION & ALGAE
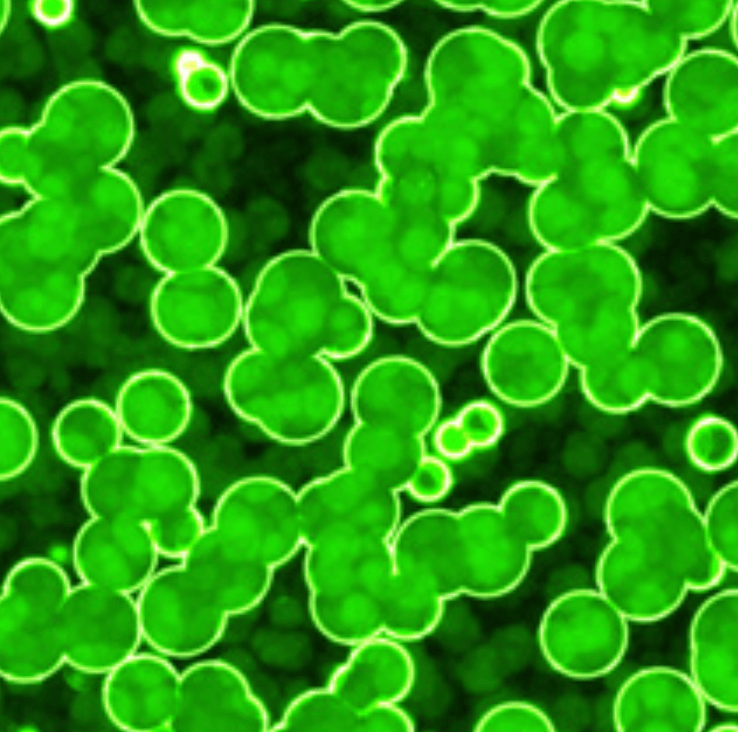
Algae represent a large group of different organisms from different phylogenetic groups, representing many taxonomic divisions. In general, algae can be referred to as plant-like organisms that are usually photosynthetic, but do not have true roots, stems, leaves, or vascular tissue, and have simple reproductive structures. They are distributed worldwide in the sea, in freshwater, and in moist areas on land. Most are microscopic, but some are quite large, such as some marine seaweeds that can exceed 50m in length.
Algae have chlorophyll and can manufacture their own food sustenance through the process of photosynthesis. Algae are just about everywhere on earth: in the sea, in rivers and lakes, on soils and walls, in animals and plants in fact just about everywhere.
Algae
In our daily life, algae which cause stains can be found on the exterior paint wall, for example. Antialgal products are used to combat Algae.